SIMPLE TESTS
CAN CONFIRM AHP
To confirm if a patient has AHP, order a random (spot) urine test for elevated levels of aminolevulinic acid (ALA), porphobilinogen (PBG), and porphyrins, the toxins that are believed to cause disease manifestations.1-6
Send the patient urine sample (preferably early morning) protected from light to a specialised laboratory and provide the laboratory with clinical details about the patient, the laboratory will perform the appropriate test.
CONFIRM THE DIAGNOSIS OF AHP WITH A RANDOM (SPOT) URINE TEST1-6
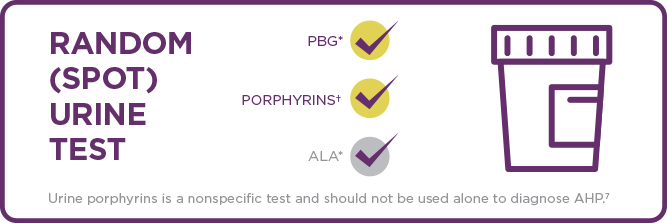
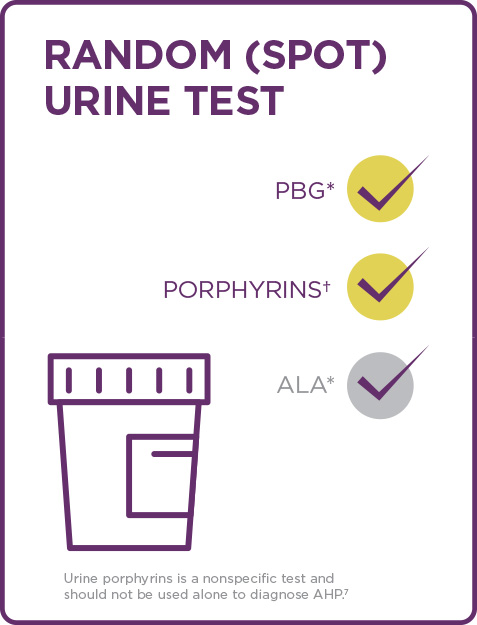
AHP=acute hepatic porphyria; ALA=aminolevulinic acid; PBG=porphobilinogen.
*PBG and ALA occur naturally in the heme biosynthesis pathway in the liver but can be toxic when elevated in patients with symptomatic AHP. PBG and ALA may remain elevated during recovery from an AIP or other type of AHP attack.2,5,8
†Urine porphyrins can help differentiate between types of AHP3
The PBG random (spot) urine test is highly specific and can confirm a diagnosis of AHP, while the ALA test is helpful for differential diagnosis and confirmation of ADP.1,5
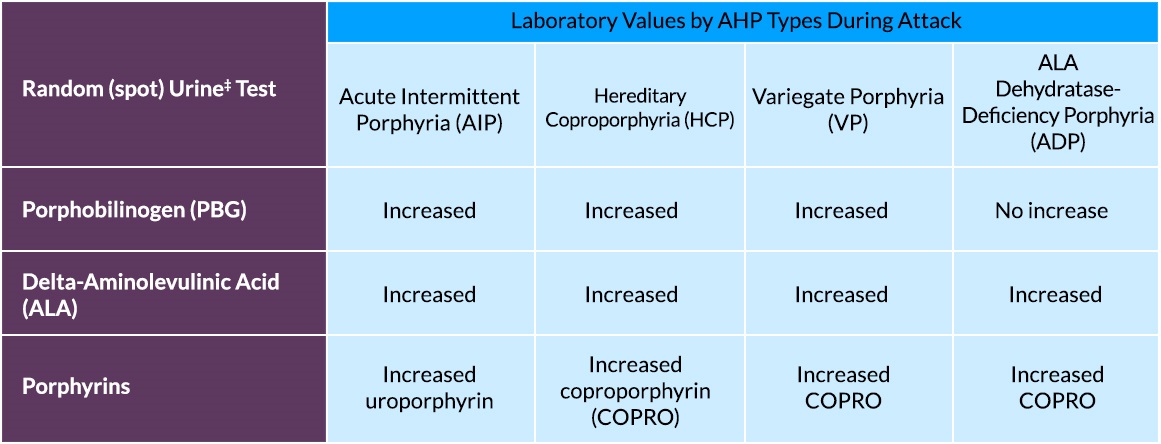
Testing for AHP: Laboratory Values1,5,9
Random Urine Test
Laboratory Values by AHP Subtypes During Attack
AIP
HCP
VP
ADP
Porphobilinogen (PBG)
Increased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Delta-Aminolevulinic Acid (ALA)
Increased
Increased
Increased
Increased
Porphyrins
Increased URP
Increased COPRO
Increased COPRO
Increased COPRO
‡Tests are more accurate when normalized per gram of urine creatinine and when sample is collected during acute episodes. 24-hour urine collection is not required. Additional testing (genetic or biochemical) may be required to differentiate AHP subtype (AIP, HCP, VP, or ADP).
- Specimen requirements are lab-specific
- During acute episodes, PBG is typically markedly elevated (>10-fold ULN) in AIP7
- Urine porphyrins are nonspecific and should not be used alone to diagnose AHP7
Samples should be collected during symptomatic periods because levels may fall when symptoms resolve. While a random (spot) urine test is key to confirming a diagnosis, a genetic test can also be performed to differentiate which type of AHP a patient may have.1,3,4
WHEN TESTING FOR AHP, ALSO
CONSIDER THE FOLLOWING:
- Ordering lab tests for urine porphyrins does not include assessment of ALA/PBG or their corresponding levels7
- ALA levels are elevated during symptomatic periods for all 4 subtypes while PBG is elevated for only the 3 most common forms (excluding ADP), but these levels may decrease between attacks7§
- Normalize test results to urine creatinine to avoid false negatives, especially in diluted urine samples3
- Urine color is normal, but can turn dark red or purple when exposed to a particular wavelength of light in a spectrum emission test4,6
- Samples should be refrigerated, frozen, and/or shielded from light, although short delays should not cause false negative results3,10
- Once a diagnosis of AHP is biochemically confirmed, gene sequencing can be used to identify the mutation and the type of AHP. Consider genetic testing of family members of patients diagnosed with AHP to identify individuals that may also carry an AHP gene mutation and potentially have elevated toxic levels of ALA and PBG3
§ALA and PBG are porphyrin precursors that occur naturally in the heme biosynthesis pathway in the liver but reach toxic levels in patients with a symptomatic AHP.2,5
WHERE TO TEST FOR AHP
UK:
Requests should be discussed in advance with the local biochemistry department who can advise on preferred porphyrin laboratory requirements. For specialised clinical and diagnostic advice consult the National Acute Porphyria Service.
Cardiff Porphyria Service
Department of Medical Biochemistry & Immunology, University Hospital of Wales, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4XW
Telephone Number (Porphyrin laboratory): 029 2074 3565
Email: porphyria@wales.nhs.uk
King's College Hospital Porphyria Service
Porphyrin Section, Reference Biochemistry, Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Viapath
King's College Hospital, London, SE5 9RS
Telephone Number (Porphyrin laboratory): 020 3299 3856
Email: kch-tr.porphyriaclinic@nhs.net
France:
Centre Français des Porphyries
The Centre de Référence Maladies Rares Porphyries / Centre Français des Porphyries (CFP) is there to help you in the management of the disease: https://www.porphyrie.net/
Un médecin du CFP est joignable 24h/24 au +33 (0)1.47.60.63.31 pour les URGENCES.
Italy:
Genilam
Genetic testing can detect certain genetic mutations in patients, and help doctors provide a more accurate diagnosis.
Access the Genilam service for acute hepatic porphyria
